ADCs Development: Our Solutions for Evaluation of Internalization Efficiency in Cancer Therapy

ADCs Development: Our Solutions for Evaluation of Internalization Efficiency in Cancer Therapy
ADCs, or antibody-drug conjugates, represent a class of targeted cancer therapies where monoclonal antibodies are chemically linked to potent cytotoxic drugs, facilitating precise delivery of the drug payload directly to cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. The selection of appropriate ADC candidates is crucial and often hinges on their internalization capacity, i.e., their ability to be taken up by cancer cells following binding to cell surface receptors.
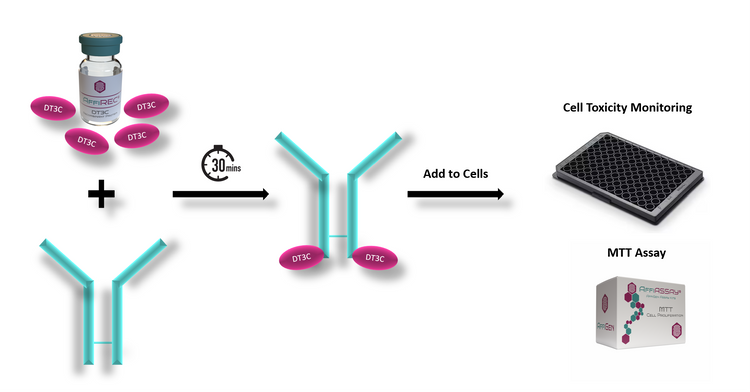
Internalization efficiency of ADCs is a critical parameter assessed during preclinical development. This process is typically evaluated using sophisticated techniques such as DT3C (Diphtheria Toxin-Based Third-Generation Circularly Permuted CAR-T Cell Therapy) coupled with the ADC. In this approach, engineered CAR-T cells expressing DT3C are utilized to assess the internalization of ADCs. The DT3C component serves as a reporter system, facilitating the quantification of ADC internalization into cancer cells.

|
AffiREC® Recombinant DT3C (Diphtheria toxin & spg 3C domain) CAT# AFG-CUB-8130 |
Upon successful internalization, the cytotoxic drug payload carried by the ADC can exert its pharmacological effect within the cancer cells. Enhanced internalization of the DT3C-ADC complex correlates with increased intracellular drug concentration, leading to potent cytotoxicity and subsequent cell death. This phenomenon is particularly advantageous as it ensures efficient delivery of the therapeutic payload to the intended target, maximizing the therapeutic efficacy of the ADC.
To quantitatively measure the impact of ADC internalization on cell viability, assays such as the MTT assay are commonly employed. The MTT assay assesses cell viability based on the ability of viable cells to convert the yellow tetrazolium salt MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) into a purple formazan dye through mitochondrial enzymes. Reduction in cell viability observed in response to ADC treatment indicates successful internalization and cytotoxicity mediated by the ADC.
In summary, ADCs rely on their ability to internalize into cancer cells for effective drug delivery and subsequent therapeutic action. Assessing ADC internalization using advanced techniques like DT3C coupled with the ADC provides critical insights into their pharmacological behavior, guiding the selection and optimization of ADC candidates for clinical development. Subsequent evaluation of cell viability using assays such as the MTT assay further validates the efficacy of ADC internalization in inducing cytotoxic effects within cancer cells.

|
AffiASSAY® MTT Cell proliferation and cytotoxicity Assay Kit CAT# AFG-EK-024 |

|
AffiASSAY® MTT Cell Proliferation Assay CAT# AFG-CBL-075 |

|
AffiASSAY® MTT Cell Proliferation Colorimetric Assay Kit CAT# AFG-BV-0473 |